medial nerve nerve root compression tests|what is deep neck compression : department Store Nerve compression syndromes can affect different peripheral nerves in your upper or lower body. Syndromes that affect your upper limbs include: Carpal tunnel syndrome: Compressed . Próximos jogos do Tottenham, resultados, vídeos, reforços, e.
{plog:ftitle_list}
Resultado da Prof. Maria Cândida Fonseca. 1977 – Admitted at the Faculté de Medecine Xavier Bichat, Université de Paris VI. 1983 – Graduated in Medicine by the Faculdade de .
what is deep neck compression
Special tests. straight leg raise. compression of lower lumbar nerve roots (L4-S1) important to distinguish from hamstring tightness. considered positive if symptoms produced with leg raised to 40°. crossed straight leg .
A nerve conduction test can detect impairment in the median nerve conduction across the carpal tunnel while having normal conduction everywhere else in its path. An EMG .
The S1 nerve root is located at the lower end of the spine, where the spine meets the pelvis. This nerve plays a vital role in controlling muscles and sensations in the legs and feet. Causes of Herniated Discs. Herniated discs .Nerve compression syndromes can affect different peripheral nerves in your upper or lower body. Syndromes that affect your upper limbs include: Carpal tunnel syndrome: Compressed .
Diagnosis. Median nerve compression syndromes include pronator syndrome, anterior interosseous nerve syndrome, and carpal tunnel syndrome. A cluster of clinical .Specific compression syndromes of the median nerve are known in the proximal forearm and at the wrist. Carpal tunnel syndrome is the best known and most common, but pronator teres syndrome and anterior interosseous nerve .Pronator syndrome (PS) is a compressive neuropathy of the median nerve in the proximal forearm, with symptoms that often overlap with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS). Because electrodiagnostic studies are often negative in PS, making . Median nerve entrapment syndrome is a mononeuropathy that affects movement of or sensation in the hand. It is caused by compression of the median nerve in the elbow or distally in the.
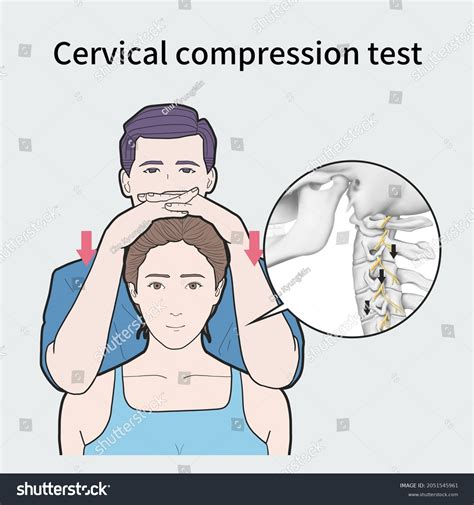
test for cervical nerve impingement
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) refers to the complex of symptoms and signs brought on by compression of the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel. . These bone spurs can narrow the foramen — the small openings on each side of your spinal column where the nerve roots exit — and pinch the nerve root. This is called foraminal stenosis. The pinched nerve root causes cervical radiculopathy. Herniated disks and cervical radiculopathy The median nerve controls movement and feeling in the forearm, wrist, hand, thumb and fingers. . arms and hands. It also sends sensory information. The brachial plexus begins as nerve roots from the cervical spine in the neck. The nerves travel . Pressure on the median nerve can cause a pinched nerve (nerve entrapment) or neuropathy (nerve .
Nerve compression syndromes of the hand present with various signs and symptoms that correspond to the nerve involved and its anatomic distribution. There are three nerves and their corresponding branches that . The median nerve is a continuation of the middle and lateral cords of the brachial plexus that receives innervation from all roots of the brachial plexus (C5-T1). After leaving the shoulder, it travels with the brachial artery under the ligament of Struthers, the bicipital aponeurosis, and the two heads of pronator teres into the anterior compartment of the forearm. . Origin and nerve roots. The median nerve arises in the axillary region and it is formed by the unification ofthe medial and lateral cords of the brachial plexus. . Test your knowledge on the arteries, veins and nerves of the elbow and forearm with this integrated quiz. . Treatment is with surgical compression. Hand of Benediction. The .
Entrapment Syndromes [edit | edit source]. There are two entrapment syndromes involving the ulnar nerve or its branches: Cubital Tunnel Syndrome - when your ulnar nerve gets irritated or compressed (squeezed) at the inside of your elbow; Guyon canal syndrome- compression of the distal ulnar nerve at the level of the wrist as it enters the hand through a space called ulnar .
Etiology. Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs most commonly in the cubital tunnel or the ulnar tunnel, i.e., Guyon's canal. At the cubital tunnel, compression between Osborne's ligament, defined as the fascia connecting the two heads of the FCU superficially and the MCL of the elbow deep, can lead to symptoms of compressive neuropathy in the forearm and hand.• Direct median nerve injury in the arm is often due to penetrating injury, and commonly associated with injury to the brachial artery as these two structures travel close together. • The median nerve is commonly noted for its susceptibility to compression neuropathy, particularly at the carpal tunnel.ULTT are performed to assess peripheral nerve mobility and compression or as a part of neurodynamic assessment. These tests are performed as a cluster to make a confirmatory diagnosis for nerve involvement. They are both diagnostic and therapeutic. Once the diagnosis is made the tests are done to mobilize the entrapped nerve.
The average sensitivity and specificity of the manual carpal compression test are 64 and 83 percent, respectively . With increased compression of the median nerve, focal demyelination can occur. . particularly with C6 or C7 nerve root involvement . The symptoms may include arm pain and paresthesia that resemble those of CTS.Rotating the head and neck to the opposite side puts the nerve under increasing stretch. If the entrapment is in the inter scalene triangle then raising the arm above the head usually increases the response. Special Test: ULTT 1 – Upper Limb Tension Test 1. PURPOSE: To test for C5, C6, C7 nerve roots and median nerve as the source of the .
Spurling test for cervical nerve root compression https: . Nerve entrapment at the medial epicondyle vs cubital tunnel. The level of compression at the Guyon’s canal. Nerve conduction studies (NCS) analyse large myelinated sensory and motor fibres, in controlled conditions. Characteristic changes to summated action potentials of sensory .syndrome occurs with compression of the median nerve between the two heads of the pronator teres (Figure 3) 42 or under the proximal edge of the flexor digitorum super-
Median nerve compression syndromes include pronator syndrome, anterior interosseous nerve syndrome, and carpal tunnel syndrome. A cluster of clinical special tests were performed to determine the anatomical site of median nerve entrapment. Based on the patient's history and clinical test results, a diagnosis of pronator syndrome was determined.
spurling test positive means
Carpal tunnel syndrome, the most common entrapment neuropathy of the upper extremity, is caused by compression of the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel. Classically, patients .Ulnar nerve entrapment occurs when the ulnar nerve is compressed. This typically occurs at two main sites: the elbow and the wrist.Ulnar nerve entrapment at the elbow is usually at the cubital tunnel (Cubital Tunnel .MRI is best for evaluating disc herniations and nerve root compression, while CT scans can help visualize the pathology causing compression of the spinal cord or nerve roots such as OPLL . NCS assess potential isolated or concomitant diagnoses of peripheral neuropathy. . Durkan’s median nerve test, and wrist flexion maneuvers will provoke . These tests can confirm or rule out ulnar nerve entrapment: Electromyography (EMG), including nerve conduction studies, measure how well signals travel through nerves to stimulate muscles. MRI , neuromuscular ultrasound or X-rays can show signs of nerve compression and help rule out problems like arthritis, ligament injuries and fractures.
The Phalen maneuver is positive if tingling is experienced when the wrist is placed at a 90° angle. With median nerve injury, specifically due to CTS, both the Tinel sign and Phalen maneuver will likely be positive. When treating median nerve compression, splinting is considered a first-line treatment.Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is caused by compression of the median nerve as it travels through the carpal tunnel. Patients commonly experience pain, paresthesia, and, less often, weakness in the .The median nerve is one of the main nerves in the hand. It originates as a group of nerve roots in the neck; these roots then come together to form a single nerve in the arm. The median nerve travels down the upper arm, across the elbow, and into the forearm, then passes through the carpal tunnel at the wrist on its way to the hand and fingers. The ulnar nerve is a sensorimotor nerve that arises from the lower trunk of the brachial plexus and converts into the medial cord, further diving into fibers of C8 and T1. It provides motor innervation to the intrinsic hand muscles, except the flexor carpi ulnaris, the flexor digitorum profundus medially, the thenar, and the lumbrical muscles. The ulnar nerve also .
Create Group Test Enter Test Code . C5-T1 roots. medial and lateral cords; Course: Anterior compartment of arm. anterior compartment (anteromedial to humerus) runs with brachial artery (lateral in upper arm / medial at elbow) . Anatomy | Median Nerve Anatomy .
The anterior interosseous nerve arises off the median nerve in the proximal forearm, approximately 5-8cm distal to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus.A 2018 cadaver study (n=50) summarized that the anterior interosseous nerve branched from the median nerve anywhere from 1.5 to 7.5 cm (mean = 5.2 cm) distal to the intercondylar line.. It is comprised of the C5-T1 . Median nerve entrapment syndrome is a mononeuropathy that affects movement of or sensation in the hand. It is caused by compression of the median nerve in the elbow or distally in the forearm or wrist, with symptoms in the median nerve distribution. . The median nerve has roots in C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1. . The pronator compression test .Radiculopathy is a mechanical compression of a nerve root usually at the exit foramen or lateral recess. . Two additional diagnostic tests that may be of use are magnetic resonance imaging and electrodiagnostic testing, consisting of NCS (Nerve conduction study) .The tibial nerve runs along the deep calf muscles with a compartment. Excessive pressure may trigger this nerve to fire uncontrollably. The TTS can be misdiagnosed for this compartment syndrome if the compression of the nerve mostly takes place near the medial malleolus. The former has also proven to be able to produce a distal tibial nerve lesion.
spurling and lhermitte's sign
bottled water ph test 2018
web7 de set. de 2023 · Os grupos de sinais na roleta são uma estratégia fascinante e envolvente para jogar este clássico jogo de cassino. Eles podem adicionar uma camada .
medial nerve nerve root compression tests|what is deep neck compression